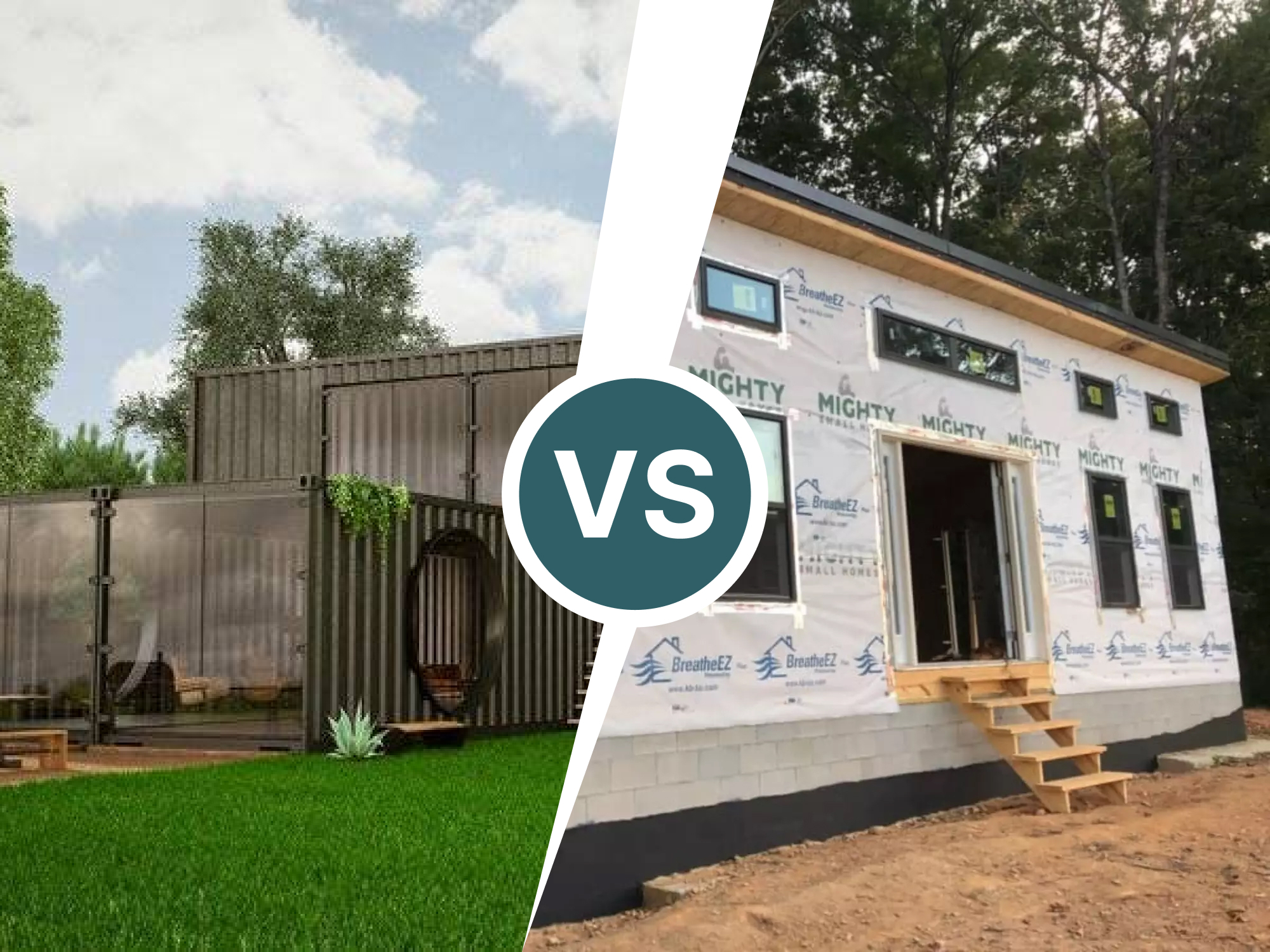
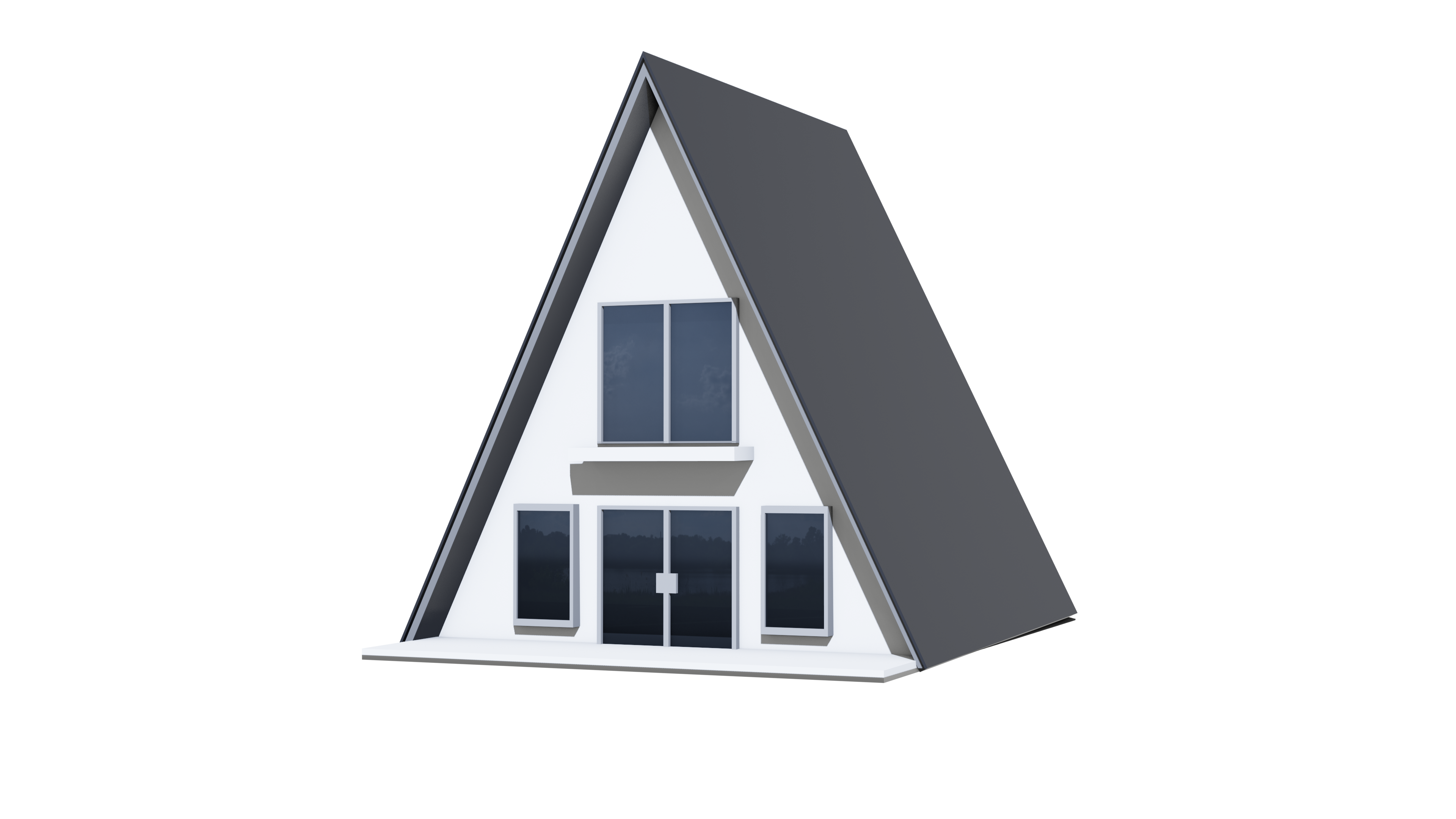
Comparing Panelized vs. Modular Prefabricated Homes
Understanding the Key Differences
A "prefabricated home" is a house that is either wholly or partially manufactured in a factory before being transported to a building site. There are two main types of prefab homes: panelized and modular. Each is built off-site but differs in construction and delivery. This article does not cover manufactured homes, also known as mobile homes, which are a separate category.
Understanding Panelized Prefabricated Homes
 A panelized house kit typically includes roof, wall, and floor systems assembled in a factory and delivered to the construction site.
A panelized house kit typically includes roof, wall, and floor systems assembled in a factory and delivered to the construction site.
Small crews assemble the wall panels on a pre-built foundation and then place the roof panels with a small boom lift. This “dry-in” step can be done in as little as two days
For example, prefab kit homes from companies like Mighty Small Homes feature strong, factory-assembled, structural insulated panels (SIPs) designed for optimal efficiency.
These panels create an airtight building envelope capable of withstanding hurricane-force winds up to 150 mph.
Homes built with SIP kits can be 2-to-3 times more energy-efficient than traditionally built homes, making them an appealing option for buyers focused on long-term durability and savings.
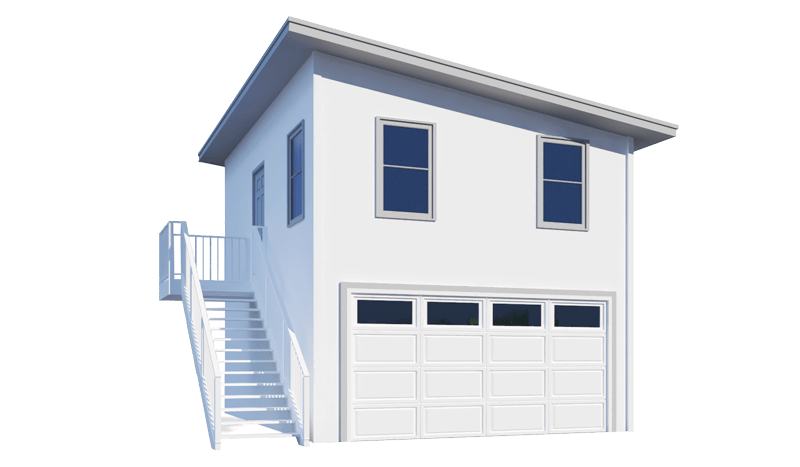
How Modular Prefabricated Homes Are Built
A modular home comprises one or more prefabricated modules grouped or stacked to form the complete structure. These modules are completely factory-built, loaded onto trucks, and assembled as units onsite. Unlike mobile or manufactured homes (often called "trailer" homes), modular homes are not designed to be moved after installation.
One modular home gaining popularity is the container-style home, constructed from repurposed shipping containers. These homes appeal to buyers seeking flexible, scalable layouts.
Key Benefits of Panelized Prefab Homes
Both panelized and modular prefab homes offer significant advantages over traditional home construction methods, ranging from faster build times to increased energy efficiency and reduced material waste. Understanding the strengths of each helps homeowners make informed decisions based on their location, budget, and design goals.
Easier Shipping and Site Access with Panelized Homes
Panelized kit homes are highly versatile, making them well-suited for various site conditions, including urban infill locations, subdivisions, and remote or hard-to-access areas.
Their lightweight, manageable components can be transported using standard trucks and assembled on-site without heavy equipment. Modular homes, by contrast, are delivered in large sections that require cranes and wide-load access, which makes them more practical for sites with established infrastructure.
Panelized Homes Save Time During Construction
Panelized and modular homes reduce on-site construction time, yet total timelines from placing an order to move-in are similar, typically 3 to 7 months, depending on design, permitting, and site conditions. Panelized SIPs homes are quickly assembled to be weather-tight in a few days and fully finished in 10-12 weeks.
Modular homes follow a comparable path, with large pre-built sections installed in days, though transport and crane logistics can stretch the schedule to 4–7 months. In contrast, traditional stick-built homes often take 7–13 months due to sequential construction and greater exposure to delays.
“People are always surprised by how fast a panelized kit goes up. We’ve had crews get a weather-tight shell up in a single day with just a few people on site, said Damian Pataluna, co-owner of Mighty Small Homes.”
Less Material Waste in Prefab Panel Construction
![]() Panelized homes benefit from factory-controlled production that reduces the amount of excess material compared to traditional stick-built methods.
Panelized homes benefit from factory-controlled production that reduces the amount of excess material compared to traditional stick-built methods.
While both modular and panelized approaches improve efficiency, panelized construction tends to result in even less on-site waste, thanks to components built to precise specifications and delivered ready for assembly.
Superior Strength of Panelized Home Construction
![]() Panelized homes, particularly those using structural insulated panels, are widely recognized for their strength and durability.
Panelized homes, particularly those using structural insulated panels, are widely recognized for their strength and durability.
They have a high-performance building envelope that resists extreme weather. Some companies like Mighty Small Homes even engineer their kits to withstand tornado and hurricane-force winds.
Modular homes, while also factory-built and often durable, vary in resilience depending on their materials and construction methods.
Though they meet or exceed building codes, they typically use conventional stick framing, which may not offer the same structural integrity as SIP-based panelized systems.
Health and Environmental Advantages of Prefab Homes
![]() Prefab homes offer clear health advantages, particularly indoor air quality, thanks to their construction in climate-controlled factories that shield materials from moisture and contaminants, reducing the risk of mold, mildew, and excessive dust.
Prefab homes offer clear health advantages, particularly indoor air quality, thanks to their construction in climate-controlled factories that shield materials from moisture and contaminants, reducing the risk of mold, mildew, and excessive dust.
Panelized homes built with airtight structural insulated panels (SIPs) take this further by limiting drafts and filtering out airborne allergens, creating healthier, more comfortable interiors.
Modular homes offer similar benefits when built with high-quality materials and modern ventilation systems.
Energy Efficiency Benefits of SIP Home Kits
![]() Panelized homes built with structural insulated panels (SIPs) are among the most energy-efficient housing systems, offering continuous insulation, airtight construction, and minimal thermal bridging that reduces heating and cooling costs by up to 60%.
Panelized homes built with structural insulated panels (SIPs) are among the most energy-efficient housing systems, offering continuous insulation, airtight construction, and minimal thermal bridging that reduces heating and cooling costs by up to 60%.
Modular homes, while factory-built and generally more efficient than traditional stick-built homes, vary in performance depending on materials and design.
Compared to conventional stick-built homes, which often lack the precision and insulation continuity of prefab methods, both panelized and modular homes offer significant energy advantages, with SIP panelized kits typically delivering the highest level of energy savings and thermal control.
Greater Design Flexibility with Panel Homes
![]() The boxy, module-based structure of modular homes often limits customization. While sleek and modern, these layouts leave less room for creativity.
The boxy, module-based structure of modular homes often limits customization. While sleek and modern, these layouts leave less room for creativity.
Panelized homes allow for nearly limitless customization, both inside and out. Most companies, including Mighty Small Homes, offer flexible floor plans to fit any lot size, aesthetic, or interior layout, making panelized homes ideal for unique design goals.
Choosing the Right Type of Panelized or Modular Home
The best choice depends on your priorities: design flexibility, energy efficiency, location, and sustainability.
Panelized kit homes offer exceptional flexibility. Their flat-packed components ship more easily to a broader range of locations, including remote, rural, or hard-to-reach areas where fully built modules might not be feasible. Because they’re assembled on-site, panelized homes also allow for greater customization in design and layout.
While often convenient and turnkey, modular homes may face limitations in where they can be delivered due to the size and transport requirements of pre-built sections. They typically require wide-load routes and specialized equipment, which can restrict placement or add cost, especially in less accessible regions.
Panelized vs Modular Homes Comparison Table
| Feature | Panelized Homes | Modular Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Method | Pre-built panels are assembled onsite. | Fully built modules are assembled onsite. |
| Customization | Highly flexible (layouts, styles, and sizes). | Limited by standard module shapes. |
| Delivery and Site Access | Delivered via standard flatbeds. Suitable for remote or tight sites | Require oversized loads and cranes. Limited by road conditions and terrain. |
| Order to Move Completion | 3-7 months | 4-7 months |
| Waste Reduction | Minimal due to factory precision | Also reduced, but more material is used |
| Energy Efficiency | Up to 60% savings with SIP home kits | Better than stick-built, but less than SIP homes |
| Durability | Strong SIP panels withstand extreme weather | Varies; often less robust |
| Indoor Air Quality | Airtight panels keep allergens out | Factory-built, but often less airtight |
Insurability of Panelized and Modular Homes
Once construction is complete, panelized and modular prefabricated homes qualify for standard homeowners' insurance.
Modular homes are treated like traditional site-built houses, offering coverage for the structure, personal property, liability, and loss of use. Panelized homes meet the same requirements, with added benefits such as energy efficiency and strong structural performance, especially when built with SIPs.
While these features may not directly lower premiums, they can influence risk assessments. Location is a key factor for both types, as remote or hard-to-access sites may affect coverage costs and availability.
Customization Options for Panelized Home Kits from Mighty Small Homes
Choosing between panelized and modular prefab homes ultimately comes down to your needs and priorities, such as customization, energy efficiency, transportation and delivery logistics, or build timeline.
“We designed these panelized kits for real people. The DIYers. The families. The downsizers. You don’t need to be a contractor to get professional results.” — Damian Pataluna
FAQs
A panelized home is constructed from factory-made wall, roof, and floor panels that are assembled onsite.
Modular homes are factory-built in modules and assembled onsite, while mobile/manufactured homes are fully constructed and movable as a whole.
Yes, but customization is often limited to standardized module shapes and layouts.
Panelized homes are more suitable for remote areas due to easier transport.
Typically, yes—especially when using SIPs (Structural Insulated Panels) like those from Mighty Small Homes.
Yes, panelized homes offer a high degree of customization in layout and style.
Panelized homes can be completed in as few as 6–10 weeks.
Depending on the builder and design, prefab houses are typically made from wood, steel, concrete, or SIPs (Structural Insulated Panels). These materials are chosen for durability, efficiency, and ease of transport.
"Prefab" is a broad term that includes modular and panelized homes. Modular homes are built in large modules and assembled onsite, while panelized homes use flat-packed wall and floor systems.
Prefab housing refers to any home built partially or entirely in a factory before being transported to the site. It includes modular, panelized, container homes, and other off-site construction methods.